تئوری میدان بلورCrystal Field Theory
An ionic theory which is an offshoot of electrostatic theory. It ignores all covalent bonding effects. It was developed by Hans Bethe in 1929 by applying group theory and quantum mechanics
to electrostatic theory. It was further developed by physicists during the 1930s and 1940s. It can be used to predict chemical properties, kinetic properties, reaction mechanisms, magnetic and spectral properties, and thermodynamic data. It cannot, however, be applied to sulfides, since sulfide forms mainly covalent bonds.
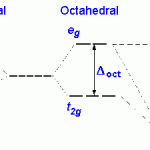
A splitting of energy levels (“crystal field splitting”) occurs because the orientation of the d orbital wavefunctions will increase an electron’s energy when the orbital is located in a region of high electron density, and lower it when the reverse is true.
برای مطالعه ادامه مطلب بر روی لینک زیر کلیک کنید.